Cannabis consumption methods are vast, and each method has its own unique effects on the body. While smoking or vaping provides rapid results, oral absorption offers a distinct experience that many consumers are turning to for its longer-lasting effects. Whether you're exploring cannabis edibles, oils, or capsules, understanding how oral absorption works can help you make informed decisions about your cannabis consumption. In this blog, we’ll dive into the science of how cannabis is processed through the digestive system, the factors that influence its effects, and how you can optimize your experience for both recreational and therapeutic use.
Consuming Cannabis: A Guide to Oral Absorption and Its Effects
With the growing popularity of cannabis for both recreational and therapeutic purposes, it's important to understand the different methods of consumption available. While smoking and vaping remain common, oral consumption of cannabis has become a preferred method for many users. In this guide, we will explore the process of oral absorption, its effects on the body, and what you need to know about consuming cannabis in this form, whether for its psychoactive or therapeutic benefits.
Does Weed Interact with Any Medications?
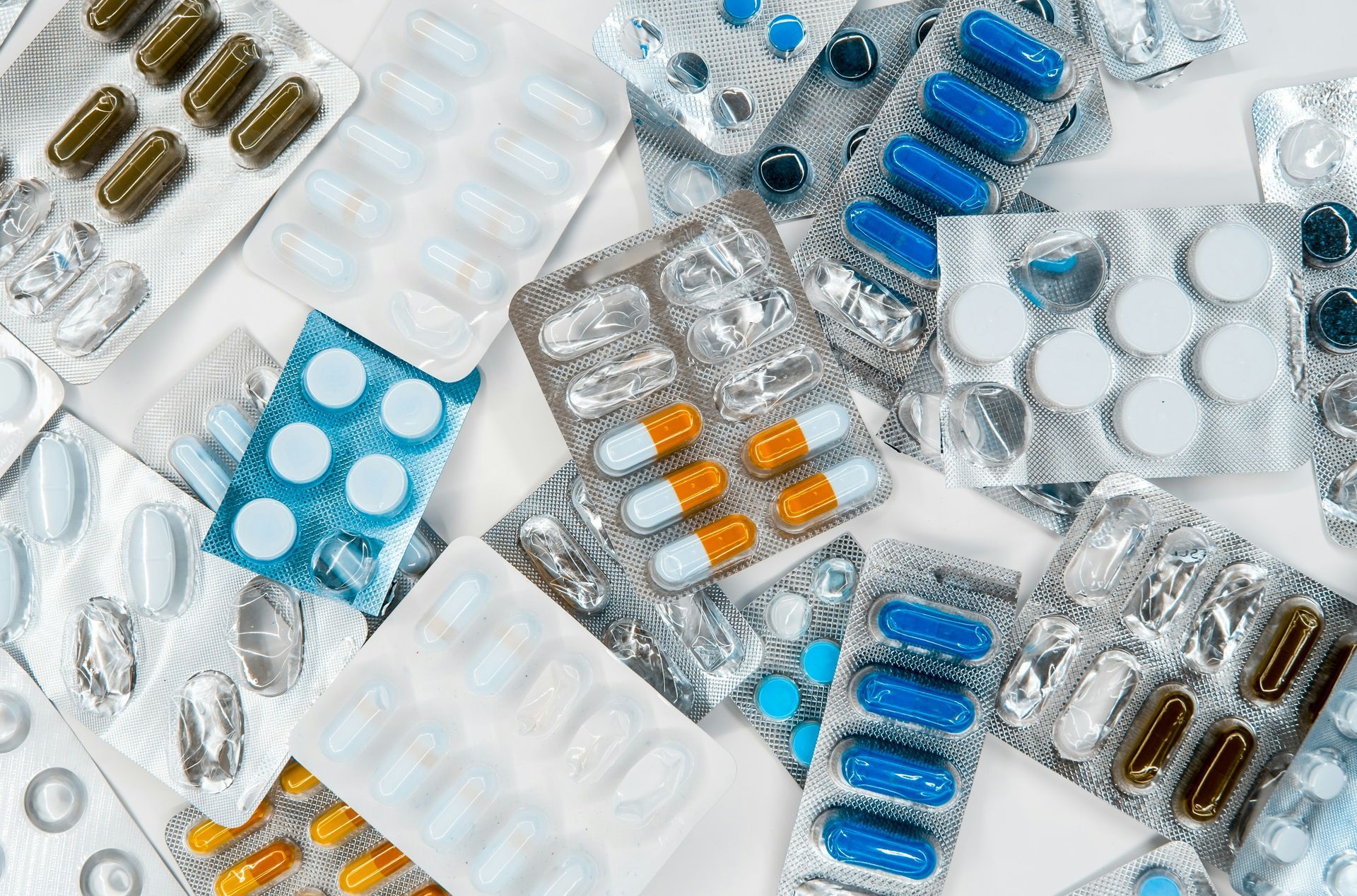
For those who use cannabis in conjunction with other medications, understanding how weed interacts with medications is essential. The body metabolizes cannabis differently depending on how it is consumed, and this can affect how it interacts with other substances. This interaction can lead to changes in the way medications work, as well as potential side effects.
Here are key insights into how weed interacts with medications, highlighting potential effects on metabolism, efficacy, and possible side effects:
Cannabis, especially when consumed orally, enters the body via the gastrointestinal tract and is metabolized by the liver. THC, the main psychoactive compound in cannabis, interacts with enzymes in the liver that also process many pharmaceutical drugs. This interaction can alter the effectiveness of medications or even intensify their effects. Additionally, CBD (cannabidiol), another key compound found in cannabis, has been known to have adverse effects on some medications, particularly those that affect the liver’s cytochrome P450 enzymes.
THC Interaction with Medications
The way THC interacts with medications largely depends on how it is consumed. When taken orally, THC undergoes first-pass metabolism in the liver, converting into 11-hydroxy-THC, a major metabolite that is much more potent than THC itself. This transformation can enhance the psychoactive effects of cannabis, but it can also impact the metabolism of other medications, possibly increasing their effects. For light cannabis users, the intensity of these interactions may be less pronounced, but the psychoactive effects could still pose challenges for those on certain prescriptions.
CBD Adverse Effects
CBD, while non-psychoactive, can influence the effects of some medications. It’s particularly important to consider if you're using drugs that interact with the liver, such as blood thinners or anti-seizure medications. CBD may increase or decrease the metabolism of these medications, potentially altering their efficacy and leading to unexpected side effects. Clinical studies on CBD and its relationship with other drugs are still evolving, but it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you plan on using cannabis with medications.
Weed and Medication Interactions
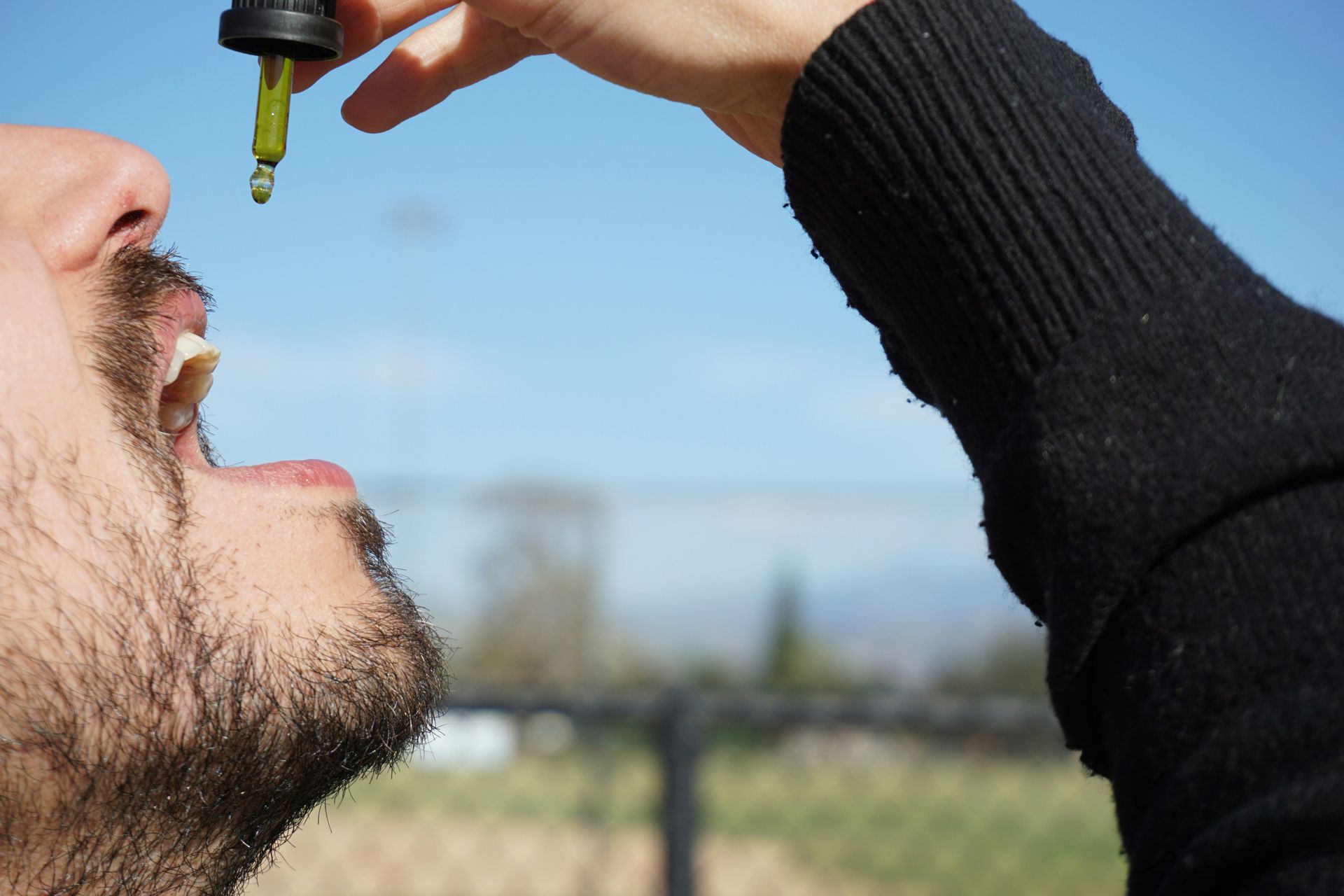
There are a variety of routes of administration for cannabis, with oral ingestion being one of the most common for both recreational and medicinal purposes. The oral administration of cannabis involves consuming edibles, oils, or capsules, which are absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. This form of consumption results in slower onset times compared to smoking or vaping, but the effects can last much longer.
Cannabis can interact with medications in a few ways:
- Metabolic Interactions: Cannabis, especially THC, can either enhance or reduce the effectiveness of certain medications by altering how they are metabolized. This is especially true when the oral dose of THC is higher, leading to stronger effects on the liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing many drugs.
- Efficacy of Medication: The interaction between cannabis and other medications can impact the therapeutic efficacy of drugs. For example, if cannabis enhances the metabolism of a medication, it may lead to reduced effectiveness, requiring dosage adjustments.
- Side Effects: Some medications, such as blood pressure medications, may have amplified effects when combined with cannabis. The physiological effects of cannabis, including its ability to lower blood pressure, can lead to dizziness or fainting when combined with certain prescription drugs.
Understanding the Effects of Cannabis
The effects of cannabis can vary greatly depending on the method of consumption. Oral cannabis preparations such as edibles or tinctures undergo a unique process of absorption, and the onset of their effects is slower compared to smokable cannabis. When taken orally, cannabis has to be digested and metabolized in the liver, where it is converted into different compounds.
Psychoactive and Physiological Effects of Oral Consumption
When cannabis is consumed orally, the body absorbs cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, which interact with cannabinoid receptors throughout the body. These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, a network of cell receptors and chemicals that help regulate various physiological functions such as pain, mood, appetite, and memory. The psychoactive effects of cannabis are often more pronounced with oral THC consumption, as the THC is converted into 11-hydroxy-THC, which has a more potent effect on the brain and body.
The psychoactive effects of cannabis can include:
- Euphoria or altered mood
- Impaired coordination and motor skills
- Increased appetite or "munchies"
- Distorted perception of time
In addition to these cognitive effects, the physiological effects of oral cannabis consumption can vary. Some users report a feeling of relaxation and relief from pain or anxiety, while others may experience dry mouth, dizziness, or an increased heart rate. The slow onset of effects is a key factor when consuming cannabis orally, which is why it’s recommended to start with a low dose and wait for the full effects before consuming more.
Clinical Effects and Studies
Clinical studies on oral cannabis consumption have highlighted the therapeutic potential of cannabis in treating various conditions, such as chronic pain, anxiety, and nausea. Cannabis has been shown to have therapeutic efficacy in the management of conditions like epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and cancer-related symptoms.
The legalization of cannabis in various parts of the world has also led to a surge in research, examining the clinical effects of cannabinoids in humans. While more research and future studies are needed, early findings suggest that oral consumption of cannabis can be an effective way to manage chronic conditions, with fewer immediate side effects compared to smoking or vaping.
Impact on Efficacy and Therapeutic Use
The impact of oral cannabis consumption on the efficacy of certain treatments can vary depending on the individual’s tolerance and the form of cannabis used. For example, cannabis edibles and oils typically provide a longer-lasting effect than smoking cannabis, making them an ideal choice for people seeking relief from chronic symptoms throughout the day. However, it is important to consider the proper dosage to avoid unwanted psychoactive effects, which can be more intense when consumed orally.
Oral cannabis preparations, such as capsules and oils, allow users to accurately control their dose, which is especially important for individuals using cannabis for medicinal purposes. The consistency of oral doses can help improve the therapeutic efficacy of cannabis in treating specific conditions, such as pain management or sleep disorders.
Factors Influencing Oral Absorption of Cannabis
Several factors influence how cannabis is absorbed and metabolized when taken orally. These include the type of cannabis product consumed, the user’s metabolism, and the presence of food in the stomach. For example, consuming cannabis on an empty stomach may lead to quicker and more intense effects, while taking it with food can slow down absorption, leading to a more gradual onset of effects.
Flavonoids in cannabis may also play a role in the absorption and experience of cannabis use. These compounds, which are present in many cannabis products, can have various health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. While the effects of flavonoids in cannabis are still being studied, they may interact with cannabinoids in ways that affect both the clinical and physiological outcomes of cannabis consumption.
The Importance of Understanding Oral Ingestion of Cannabis
Oral ingestion of cannabis has both its advantages and challenges. For those seeking longer-lasting effects without the harshness of smoking, oral consumption is a great option. However, the delayed onset of effects can lead to overconsumption if users are not mindful of their dosage. It is always essential to start with a small oral dose and give it time to take effect before consuming more.
Ultimately, the experience of cannabis use is highly individualized, and understanding the impacts of oral THC consumption, as well as the various cannabis products available, can help users make informed decisions. Whether you're a first-time user or an experienced consumer, knowing how cannabis interacts with your body is key to maximizing its benefits and minimizing unwanted effects.
Conclusion
Cannabis, particularly when consumed orally, offers a unique and long-lasting experience for both recreational and medicinal users. As cannabis legalization continues to expand globally, more research will undoubtedly shed light on its clinical effects and the impact of various consumption methods on the human body. In the meantime, understanding the routes of administration and how cannabis interacts with medications is vital for safe and effective use. By considering factors such as THC interaction with medications, the effects of cannabis, and the cannabis product characteristics, users can enjoy the therapeutic and psychoactive benefits of cannabis in a controlled and informed manner.